Unemployment benefits are monetary payments made by the state or other certified bodies to laid-off people. These benefits are provided depending on the status of the unemployed person, and to those who get themselves listed as unemployed, and who are seeking a job. The state offers unemployment benefits through insurance programs within rules set by Federal Law, to its nationals who apply for it. The state law also decides the ability for unemployment insurance, benefit amounts and duration for which benefits are obtainable.
How Much can you Receive as Unemployment Compensation?
Unemployment benefits are planned to partially restore lost wages, so the exact amount you receive will be based on what you used to earn. States employ special formulae to compute benefit payments, but all states take earlier earnings into account in some way. Some states think the employee’s previous annual earnings while others look at the employee’s earnings during the highest paid quarter or two quarter of the base period.
All states also place an upper limit on the weekly benefit amount. A common formula is to pay half of what of what the employee used to earn, up to a cap that’s tied to the average earnings in that state. This means that employees with higher wages may collect a larger overall benefits check, but a lesser percentage of what they used to earn. The highest amount an employee can obtain each week differs widely from state to state.
Some states offer an additional benefit amount to employees with dependents but these tend to be small.
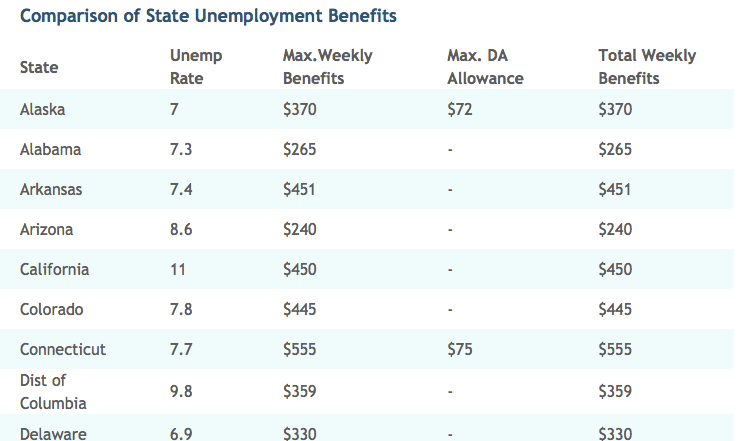
State Unemployment Benefits Comparison
The top states which pay highest unemployment compensation are Massachusetts ($939) followed by Rhode Island ($688), then Connecticut ($630), New Jersey ($611) and Pennsylvania ($581).
The top states that pay the lowest unemployment compensation are Mississippi ($235), Arizona ($240), Louisiana ($247), Alabama ($265) and Florida – $275 respectively.
This following table provides a complete list of unemployment benefits and duration for all states.
NOTE: for remaining states, check Unemployment Benefits Comparison by State
How to Calculate Unemployment Benefits?
We have developed Unemployment Calculator that gives you an estimate of your benefits.
If you would like to understand how benefits amount is calculated, here are the steps involved:
- Assess your state’s unemployment insurance rules. Get in touch with the workforce division and inquire what formula is currently being used to compute weekly benefit rates (WBRs). States may vary a little on how unemployment benefits are figured. In addition to the formula, request the state for the maximum and the minimum WBRs. For purposes of this example, assume the maximum WBR is $600 and the minimum is $25.
- Find out your base period. The base period is a set of months used to compute your WBR. It is generally the last four out of five calendar quarters.
- Average your earnings during the base period. You can do this by summing up the wages earned in each month and dividing it by the applicable number of months. Some states may only use the average of the highest two months during your base period, such as Colorado. Other states such as New Jersey, multiply the average by a exact percentage (60% in New Jersey). For purposes of this article, average the complete the base period and multiply it by 60. Presume the average wages you received all through your period is $12,000. Multiply $12,000 by 60; the end result is $7,200
- Divide the averaged wages by 26 (which represent the number of weeks you can stay on unemployment). The result must be equivalent to or more than the minimum WBR and it cannot go beyond the maximum WBR i.e. $600 here. In this example, you would be entitled to approximately $276 per week in benefits ($7,200 divided by 26).
Weekly Compensation
Every state sets an upper limit on the total weekly benefit amount. A common formula is to give half of what the employee used to receive. This means that employees with higher wages may obtain larger overall benefits check, but a lesser percentage of what they used to earn. The highest amount an employee can obtain each week differs extensively from state to state.
Dependent Allowance
Some states offer an additional benefit amount to employees with dependents. These amounts tend to be less; most states that provide this benefit offer $25 per dependent per week in added benefits. Unemployment benefits are chargeable. You may opt to have up to 10% of your benefit amount withheld to pay federal income taxes.
What if you work part-time during unemployment?
If you receive other income while receiving unemployment, that may lessen the amount of benefits obtainable to you. Certainly, if you find a new job, you will no longer be entitled for unemployment. But if, for instance you pick up temporary work for a day or two while you are otherwise without a job, you must report your earnings to the state unemployment agency, which will decide whether your unemployment benefits must be reduced to reflect those earnings.
How Do You Get Unemployment Benefits?
Eligibility
Before you learn more about unemployment benefits, check unemployment eligibility article to make sure you are qualified to receive unemployment benefits. You ought to qualify for gaining these compensation benefits, people who fail short to earn wages during one year, or are jobless through no fault of their own come under the general eligibility criteria.
Ineligibility from gaining unemployment benefits can occur if you quit a job without good reason, have resigned due to illness, are fired for misconduct, have become self-unemployed, have left the job for getting married, have been a part of a labor argument or have left due to educational engagements.
Usual benefits are paid for a maximum of 26 weeks in most of the welfare states. In numerous states the repayment in monetary terms is half of the earning of an average working person, for instance in New York, $405 is provided to the unemployed mass which is half of the state’s average weekly wage of a working person.
Apply For Benefits
In case you fall under the qualifying criteria for unemployment benefits you can apply online or via telephone or you can visit your state unemployment office for claiming them. In order to claim the benefits you require; social security number, alien registration card (if not a US citizen), telephone numbers, Names, postal mailing address including zip code, addresses and dates of employment of all your past employers for the last two years. It hardly takes two weeks for getting the pay check of compensation after you have claimed for these benefits, direct deposit or debit card. If your claim is accepted once, you can file for these benefits very easily, by just a single call of email. You have the right to request the denial of your unemployment claim, if your claim is refused by your employer.
Additional Eligibility Criteria
The states that offer such benefits to the masses normally require that the person obtaining these benefits must continue his/her hunt for finding a job. They want an assurance that the recipients of unemployment benefits must be ready, willing, available, and able to work whenever he/she finds a job. Furthermore the states may also require unemployed people to enthusiastically apply for jobs, submit resumes, and not refuse if it seems appropriate for them.
Unemployment Insurance – Other Benefits
Financial assistance is just one part of unemployment insurance benefits. There are numerous other benefits such as Job Search Assistance, Career Coaching, and Extension of Unemployment Benefits beyond standard 26 weeks during times of high unemployment.
The idea of unemployment insurance program is not only to give temporary living assistance, but able to guarantee that the job market is stable and sustainable. For this reason, most of the State Unemployment Insurance Programs offer quite a few benefits other than the monetary assistance.
Job Search Assistance
State Unemployment Agencies assist you get an appropriate job by providing job aid tools. Such tools will help you look for job openings, build resume, research current wage information etc. In addition, you can obtain industry and job-related trends, and recognize career opportunities in new fields.
The Employment Interviewer will review your education/work history and help match your skills to jobs obtainable in our area. They are in close contact with local employees and in tune with the local labor market. They can hunt their databank for jobs that interest you and, if you meet the employer’s qualifications refer you to job openings. If possible, they may even plan an interview for you!
Career Coaching
Numerous states offer career coaching services. Workshops and training sessions are available for workers who have become unemployed so that they can develop their current skills or learn new ones. Continually expanding skills helps to increase the chances of finding new jobs and probably achieve success all through the career.
Please realize that not all programs are provided free, however states negotiate fees with training institutions just for you. Get in touch with state unemployment offices to ask about the expenses and make the best use of these programs.
Extension of Unemployment Benefits
In a normal economic climate, nearly all states offer unemployment benefits for up to 26 weeks, or half a year, though a handful of states now provide benefits for fewer weeks. However, the total period for which a former employee can obtain benefits has been extended several times, through two separate programs. Based on when and where the employee began collecting unemployment, an employee might be qualified to collect benefits for up to 73 additional weeks. The cost of the “extended benefits” is paid regularly from state and federal funds.

Comments are closed.